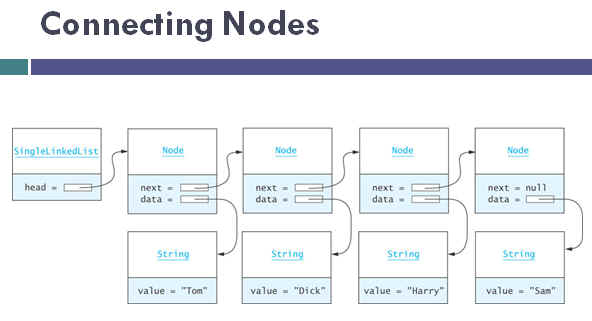
|
private static class Node<E> {
private E data; /**The data value. */
private Node<E> next = null; /** The link */
/**
* Construct a node with the given data value and link
* @param data - The data value
* @param next - The link
*/
private Node(E data, Node<E> next) {
this.data = data;
this.next = next;
}
/**
* Construct a node with the given data value
* @param data - The data value
*/
private Node(E data) {
this(data, null);
}
}
|
static nested class does
not have access to other members of the enclosing class. That is,
The
keyword static
indicates that the Node<E>
class
will not reference its outer class.
non-static nested class is an inner class. For
example,
public class ShadowTest {
public int x = 0;
class FirstLevel {
public int x = 1;
void methodInFirstLevel(int x) {
System.out.println("x = " + x);
System.out.println("this.x = " + this.x);
System.out.println("ShadowTest.this.x = " + ShadowTest.this.x);
}
}
public static void main(String... args) {
ShadowTest st = new ShadowTest();
ShadowTest.FirstLevel fl = st.new FirstLevel();
fl.methodInFirstLevel(23);
}
}
/*
The following is the output of this example:
x = 23
this.x = 1
ShadowTest.this.x = 0
*/