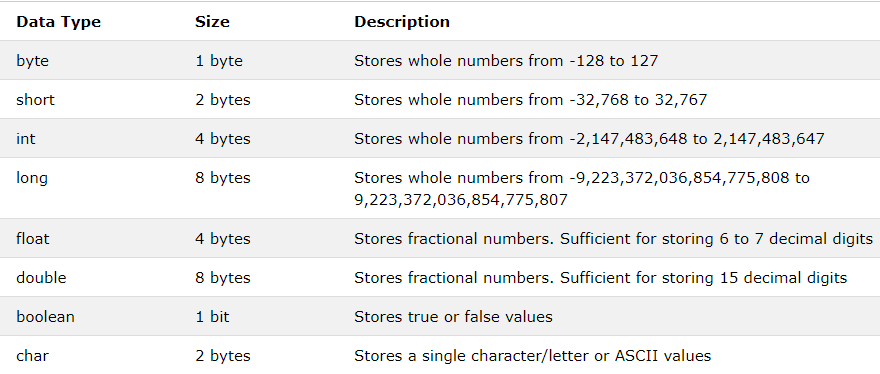
A primitive data type specifies the size and type of variable values, and it has no additional methods.
There are eight primitive data types in Java:

Variables are containers for storing data values.
A label of a memory box.
Associate data type with variable name.
For example,
int num; //Integer (whole number)
float price; //floating point number
char grade; //character
boolean done; //boolean
Given a beginning value for a variable.
int num = 100; //Integer (whole number)
float price = 2.59; //floating point number
char grade = 'B'; //character
boolean done = true; //boolean