Three types of selection statements.
if statement:
if…else statement:
switch statement:
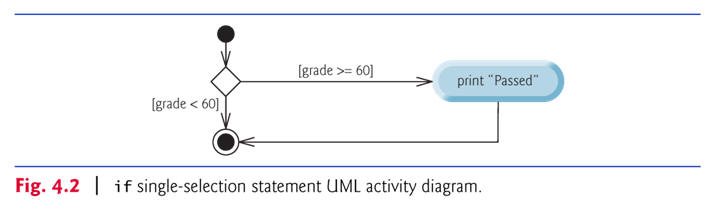
if Single-Selection Statement

|
Pseudocode:
If student’s grade is greater than or equal to 60 |
Java Code:
if
( studentGrade >=
60
) |
| If the condition is false, the Print statement is ignored, and the next pseudocode statement in order is performed. | |
Indentation
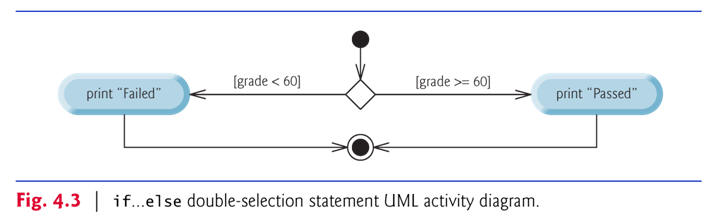
if…else Double-Selection Statement
if…else double-selection statement—specify an action to perform when the condition is true and a different action when the condition is false.
|
Pseudocode:
If student’s grade is greater than or equal to 60 |
Java Code:
if
( grade >=
60
) |
| Note that the body of the else is also indented. | |
Conditional operator (?:)—shorthand if…else.
Ternary operator (takes three operands)
boolean expression ? the value if the boolean expression is true : the value if the boolean expression evaluates to false
System.out.println(studentGrade >= 60 ? "Passed" : "Failed" );
Nested if else statement:
Need else or not? (click it)
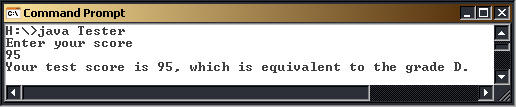
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Tester
{
public static void main(String [] args)
{
int score ;
char grade;
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter your score");
score = input.nextInt();
if (score >=90)
grade = 'A';
else if (score >=80)
grade = 'B';
else if (score >=70)
grade = 'C';
else if (score >=60)
grade = 'D';
else
grade = 'F';
System.out.println("Your test score is "+ score
+ ", which is equivalent to the grade " + grade + ".");
}
}
|
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Tester
{
public static void main(String [] args)
{
int score ;
char grade;
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter your score");
score = input.nextInt();
if (score >=90)
grade = 'A';
if (score >=80)
grade = 'B';
if (score >=70)
grade = 'C';
if (score >=60)
grade = 'D';
else
grade = 'F';
System.out.println("Your test score is "+ score
+ ", which is equivalent to the grade " + grade + ".");
}
}
|
 |
A ticket for a movie costs (i) $10 for a person who is older than 13; (ii) $6 for a senior who is 60 or older (iii) $0 for a kid who is 13 or younger.
What is wrong with the following segment?
if(age > 13)
ticketPrice = 10;
else
if(age > = 60)
ticketPrice = 6;
Click here for Nested If-Else.
Click here for dangling else problem
Click here for switch statement