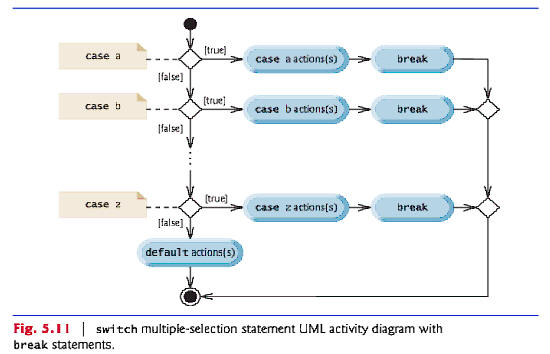
switch Multiple-Selection Statement
switch multiple-selection statement performs different actions based on the possible values of a constant integral expression of type byte, short, int or char.
Click here for additional information.
// Fig. 5.9: GradeBook.java
// GradeBook class uses switch statement to count letter grades.
import java.util.Scanner; // program uses class Scanner
public class GradeBook
{
private String courseName; // name of course this GradeBook represents
// int instance variables are initialized to 0 by default
private int total; // sum of grades
private int gradeCounter; // number of grades entered
private int aCount; // count of A grades
private int bCount; // count of B grades
private int cCount; // count of C grades
private int dCount; // count of D grades
private int fCount; // count of F grades
// constructor initializes courseName;
public GradeBook( String name )
{
courseName = name; // initializes courseName
} // end constructor
// method to set the course name
public void setCourseName( String name )
{
courseName = name; // store the course name
} // end method setCourseName
// method to retrieve the course name
public String getCourseName()
{
return courseName;
} // end method getCourseName
// display a welcome message to the GradeBook user
public void displayMessage()
{
// getCourseName gets the name of the course
System.out.printf( "Welcome to the grade book for\n%s!\n\n",
getCourseName() );
} // end method displayMessage
// input arbitrary number of grades from user
public void inputGrades()
{
Scanner input = new Scanner( System.in );
int grade; // grade entered by user
System.out.printf( "%s\n%s\n %s\n %s\n",
"Enter the integer grades in the range 0-100.",
"Type the end-of-file indicator to terminate input:",
"On UNIX/Linux/Mac OS X type <Ctrl> d then press Enter",
"On Windows type <Ctrl> z then press Enter" );
// loop until user enters the end-of-file indicator
while ( input.hasNext() )
{
grade = input.nextInt(); // read grade
total += grade; // add grade to total
++gradeCounter; // increment number of grades
// call method to increment appropriate counter
incrementLetterGradeCounter( grade );
} // end while
} // end method inputGrades
// add 1 to appropriate counter for specified grade
private void incrementLetterGradeCounter( int grade )
{
// determine which grade was entered
switch ( grade / 10 )
{
case 9: // grade was between 90
case 10: // and 100, inclusive
++aCount; // increment aCount
break; // necessary to exit switch
case 8: // grade was between 80 and 89
++bCount; // increment bCount
break; // exit switch
case 7: // grade was between 70 and 79
++cCount; // increment cCount
break; // exit switch
case 6: // grade was between 60 and 69
++dCount; // increment dCount
break; // exit switch
default: // grade was less than 60
++fCount; // increment fCount
break; // optional; will exit switch anyway
} // end switch
} // end method incrementLetterGradeCounter
// display a report based on the grades entered by user
public void displayGradeReport()
{
System.out.println( "\nGrade Report:" );
// if user entered at least one grade...
if ( gradeCounter != 0 )
{
// calculate average of all grades entered
double average = (double) total / gradeCounter;
// output summary of results
System.out.printf( "Total of the %d grades entered is %d\n",
gradeCounter, total );
System.out.printf( "Class average is %.2f\n", average );
System.out.printf( "%s\n%s%d\n%s%d\n%s%d\n%s%d\n%s%d\n",
"Number of students who received each grade:",
"A: ", aCount, // display number of A grades
"B: ", bCount, // display number of B grades
"C: ", cCount, // display number of C grades
"D: ", dCount, // display number of D grades
"F: ", fCount ); // display number of F grades
} // end if
else // no grades were entered, so output appropriate message
System.out.println( "No grades were entered" );
} // end method displayGradeReport
} // end class GradeBook
// Fig. 5.10: GradeBookTest.java
// Create GradeBook object, input grades and display grade report.
public class GradeBookTest
{
public static void main( String[] args )
{
// create GradeBook object myGradeBook and
// pass course name to constructor
GradeBook myGradeBook = new GradeBook(
"CS101 Introduction to Java Programming" );
myGradeBook.displayMessage(); // display welcome message
myGradeBook.inputGrades(); // read grades from user
myGradeBook.displayGradeReport(); // display report based on grades
} // end main
} // end class GradeBookTest

The expression in each case can also be a constant variable—a variable that contains a value which does not change for the entire program. Such a variable is declared with keyword final.